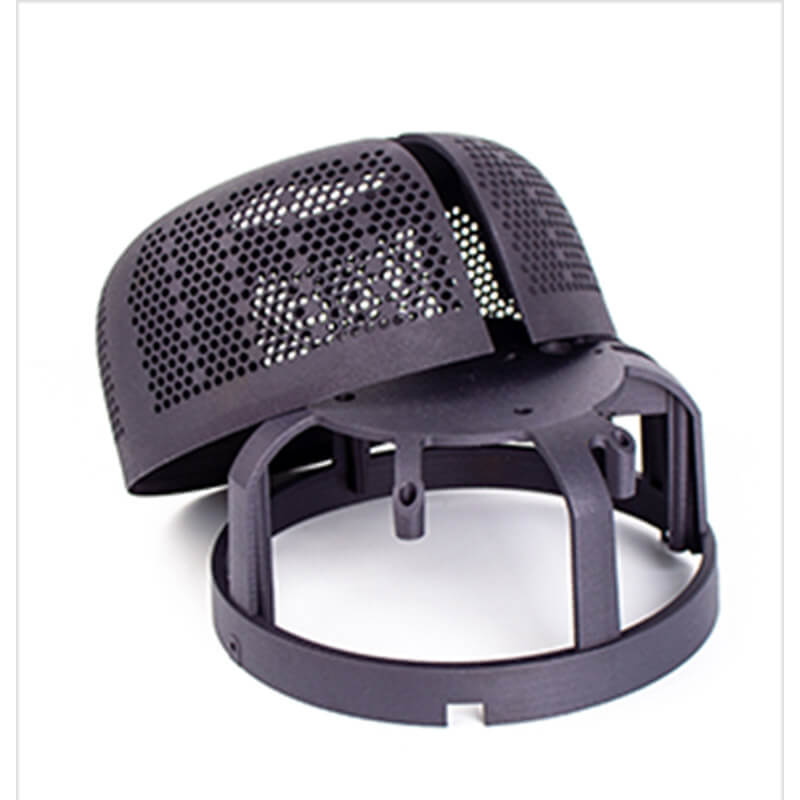
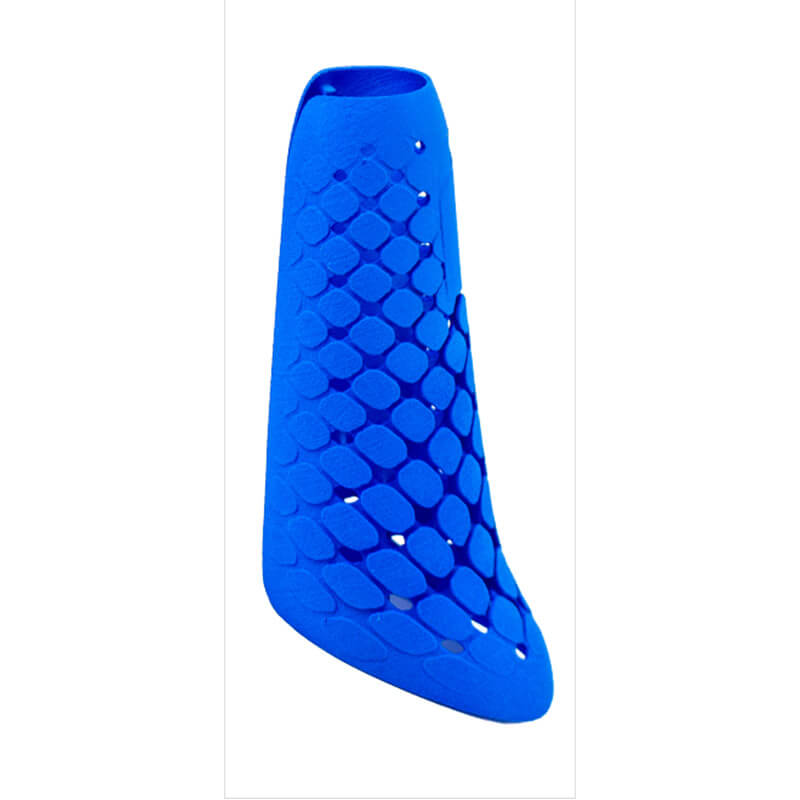
Selective Laser Sintering
Selective Laser Sintering
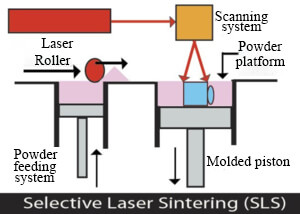
Similar to the SLA photopolymerization process (resin printing), SLS also utilizes laser curing of the entire substance. The difference lies in the use of infrared laser beams in SLS, and the material shifts from photosensitive resin to composite materials like plastics, wax, ceramics, metal powder, or nylon powder. Initially, a very thin (sub-millimeter) layer of raw powder material is not spread on the worktable. It is then scanned by a computer-controlled laser beam through a 3D scanner at a specific speed and energy density to layer the two-dimensional data. The laser-scanned powder is sintered into a solid layer of a certain thickness, while the unscanned areas remain as loosely packed powder.
SLS Technology Schematic
Working Principle:
The powder is preheated to a temperature slightly below its melting point, then leveled using a roller or scraper. Under computer control, a high-intensity CO2 laser selectively sinters parts based on layered cross-sectional information. The sintered material adheres to the formed part below, and the process repeats layer by layer. Once all the sintering is complete, excess powder can be removed, leaving the sintered portion.

Pros and Cons

Advantages
- Suitable for complex structures and unique geometries, nylon 3D printing supports small-batch/customized production.
- Excellent material strength without the need for added processing supports.
- Short processing cycles, low costs.
- Optimized structures and open-minded thinking.
Disadvantages
- Surface quality not as high as SLA resin 3D printing.
- Available materials are temporarily limited by industry applications.

Optional Materials

PA2200 Nylon Material
- Performance: Excellent strength, can undergo secondary processing and assembly, white appearance
- Typical Applications: 3D printed external display components, casings.
PA3200 Nylon Glass Fiber Material
- Performance: High strength, can undergo secondary processing and assembly, white appearance
- Typical Applications: 3D printed external display components, casings.

Application Scope
- Validate functional tests, such as prototypes for appearance or R&D design.
- Small-batch customization/personalization, including 3D printing for custom gifts.
- Suitable for industries requiring precision and complex structures, such as aerospace, medical, molds, and 3D printing surgical guides.
Explore Other Products

Automatic Lathe
Test Pin and other Automatic Lathing Machining Parts such as screws,copper pillar, knob, etc.

CNC Milling & Turning Combination
Roller shaft,Turn-milling composite processing, 7075 aluminum machining, and another turning and milling CNC machining parts.

Sheet Metal Fabrication
New Energy Battery Casing and other differentSheet Metal Fabrication parts such as Housing, Case,Enclosure, etc.






