CNC FR4 Machining
CNC FR4 Machining
FR4 boards, made from a composite of glass fiber cloth and epoxy resin (with “FR4” denoting the cloth specification), come in common thicknesses of 1.6mm and 1.2mm. They are also referred to as “glass fiber” or “epoxy resin boards” and serve as insulators. Notable attributes include high-temperature resistance (180~200°C), moisture resistance, strong mechanical properties, and good dielectric performance. Common colors for FR4 boards are white, yellow, black, and light green. FR4 CNC machining centers offer high precision (within 0.02mm), smooth edges, no burrs, and no machining traces. These boards are widely used in electronic manufacturing due to their excellent electrical properties, mechanical performance, and chemical stability. Moreover, they provide superb insulation and high-temperature resistance, making them suitable for high-temperature and

Surface Finishes after CNC FR4 Machining
| Picture | Surface finishes | Machining principle | Material | Colors | Texture | More |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
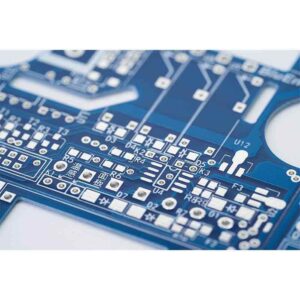 | Tin solder Coating | Tin solder coating of FR4 typically involves applying a thin layer of tin to the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB) that is made from FR4 (Flame Retardant 4) material. | Tin | Silver | Glossy | Learn More |
 | Golden solder Coating | Golden solder coating, also known as gold plating or gold finish, of FR4 refers to the application of a thin layer of gold onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB) made from FR4 (Flame Retardant 4) material. | Gold | Golden | Glossy | Learn More |
 | Silver solder Coating | Silver solder coating, or silver plating, of FR4 refers to the application of a thin layer of silver onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB) made from FR4 (Flame Retardant 4) material. | Silver | Silver | Glossy | Learn More |
Some Picture CNC FR4 machining Parts
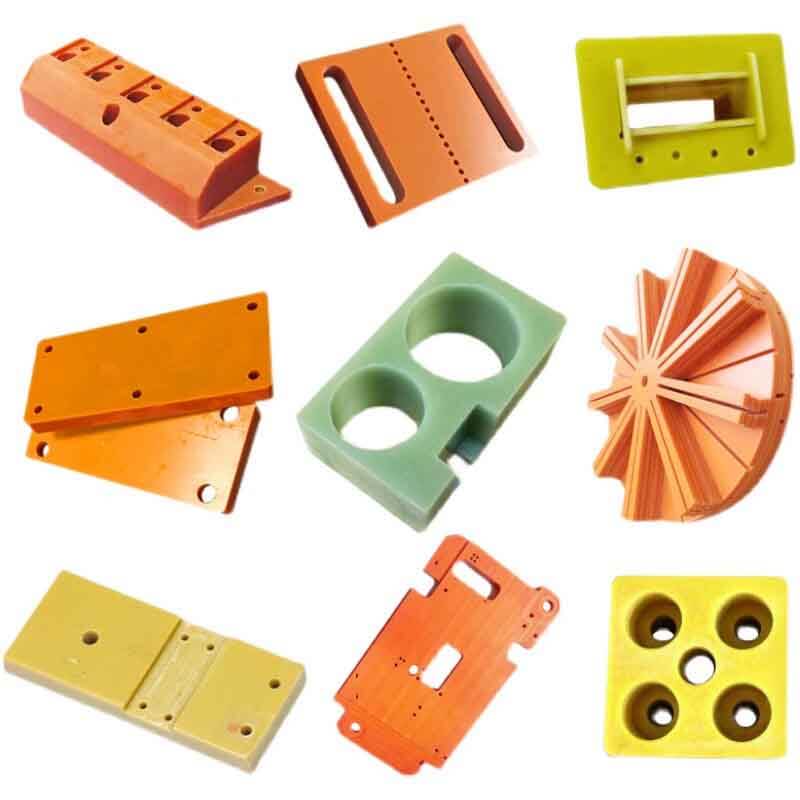
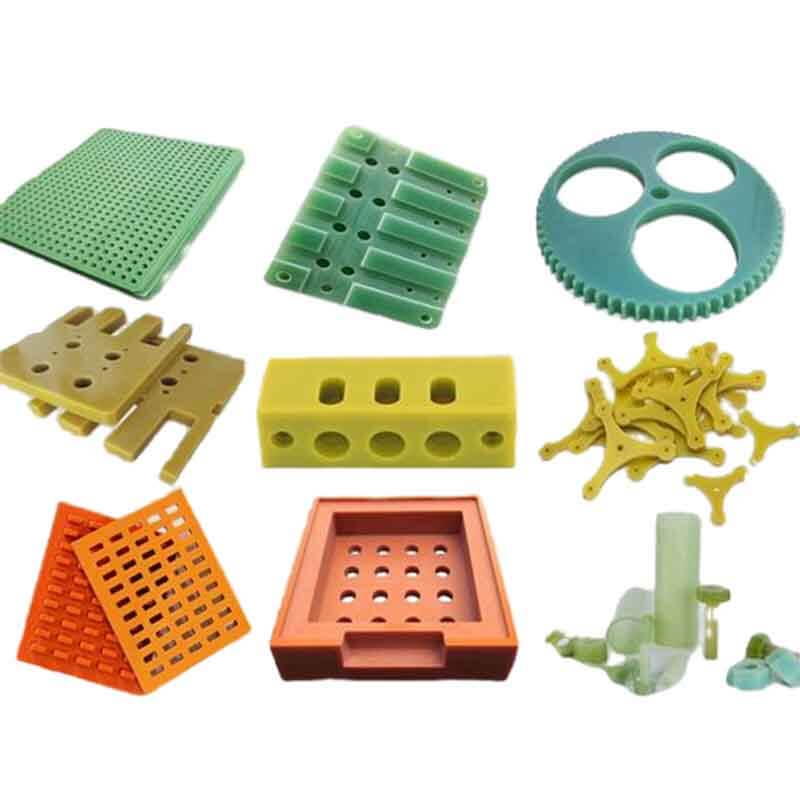
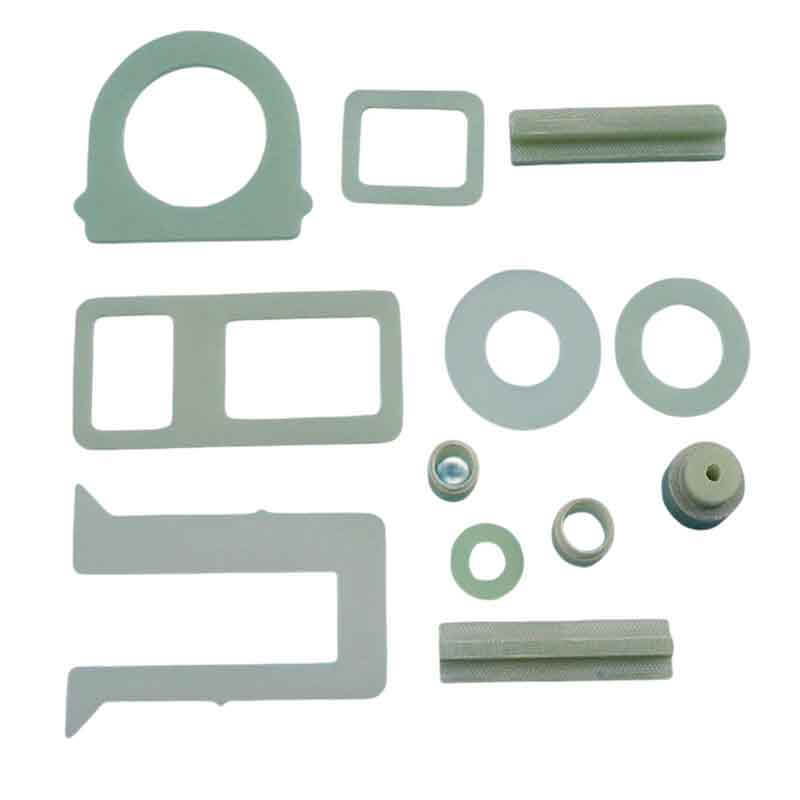
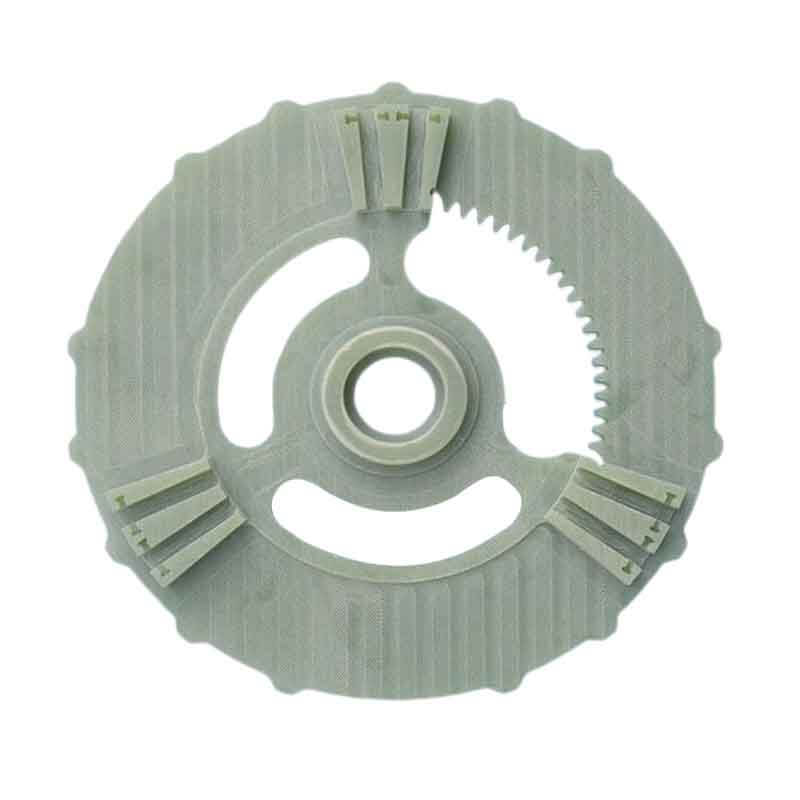
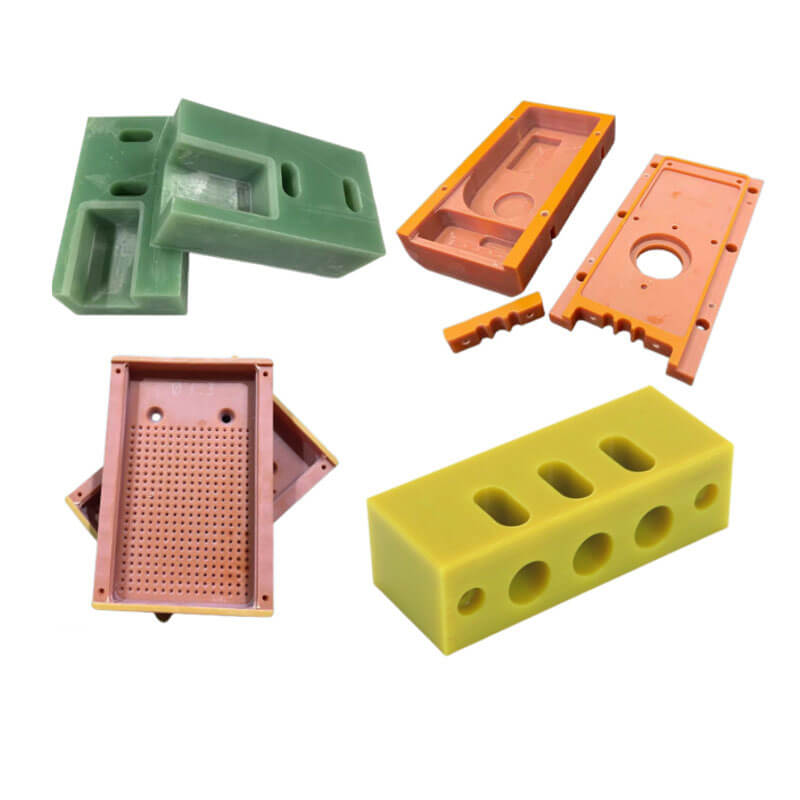






CNC FR4 Machining FAQs
CNC machining of FR4 (Flame Retardant 4) is a common process used in the fabrication of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and various electronic components.
Yes, CNC machining can be used for both single-sided and double-sided PCBs. For double-sided PCBs, the CNC machine can drill through holes and create vias to connect traces on both sides of the board.
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety goggles and dust masks, to protect against dust and debris.
Ensure proper ventilation and dust collection systems to minimize exposure to airborne particles.
Follow machine-specific safety guidelines and use safety guards when operating CNC machines.
Yes, there are alternative methods for PCB fabrication, such as chemical etching and 3D printing, but CNC machining is a popular choice due to its precision and versatility.
1) Outstanding Performance Stability
FR4 boards exhibit extremely high stability and a long operational lifespan, allowing them to function reliably in high-temperature and high-pressure environments. Furthermore, they can resist interference from electromagnetic and radiation sources, effectively preventing a decline in insulation performance.
2) Exceptional Mechanical Strength
FR4 boards can withstand mechanical stresses such as impact, vibration, and pressure and possess excellent resistance to acids, alkalis, and corrosion. This makes FR4 boards suitable for long-term stable operation not only at normal temperatures but also in various harsh environmental conditions.
- High-Precision Machining Capabilities
FR4 boards have a certain level of machining capabilities, meeting the requirements of different customers. Additionally, they can undergo processes such as drilling, boring, circuit cutting, and surface mounting, enabling the achievement of high precision and low error in manufacturing processes.
FR4 boards have a wide range of applications and are primarily used in the fields of electronics, electrical engineering, telecommunications, aerospace, and more. The following are their main applications:
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
In electronic manufacturing, FR4 boards are commonly used in the production of printed circuit boards. They serve as the substrate material for PCBs, ensuring the stability and reliability of the circuit boards.
- Insulation and Barrier Materials
Due to the exceptional insulation performance and high-temperature stability of FR4 boards, they can be used as insulation and barrier materials in power systems. This not only guarantees the electrical safety of equipment but also helps prevent accidents caused by electrical faults.
- Mechanical Components
FR4 boards can also be employed as materials for mechanical components, such as machine tool partitions and automobile engine covers. They possess outstanding mechanical properties and chemical stability, making them suitable for various mechanical
Free Sample
Explore More Plastic Materials

Nylon CNC Machining
Nylon is abbreviated as PA in English, and its full name is Polyamide. There are various types of nylon, including PA6, PA66, PA610, PA11, PA12, PA1010, PA612, PA46, and more.

PC CNC Machining
PC sheets, also known as polycarbonate sheets or polyester sheets, are characterized by high transparency, lightweight, impact resistance, sound insulation, heat insulation, flame resistance, and resistance to aging. They are

CNC FR4 Machining
FR4 boards, made from a composite of glass fiber cloth and epoxy resin (with “FR4” denoting the cloth specification), come in common thicknesses of 1.6mm and 1.2mm. They are also

