Mill Turn Machining Parts
Mill Turn Machining Parts
Stainless steel turning milling parts manufacturer in China.
MOQ Starts from 1pcs.
As a specialized cnc turning milling parts manufacturers,Masion provides high-quality custom different cnc turning milling parts services to customers with outstanding production advantages, advanced technological capabilities, and professional solution offerings.

Masion Capability
High Capacity, Proper Price
10000pcs production capacity per month make the price lower.
Free Samples, Low MOQ
1pcs MOQ make you order flexibly with one free sample for you testing.
Certified Factory, Guaranteed Quality
ISO9001:2008 and strictly 100% inspection guarantee quality and CMM inspection equipment.
High precision, thick gold
With 0.005mm tolerance and with different surface finishing and different materials.
Our Products
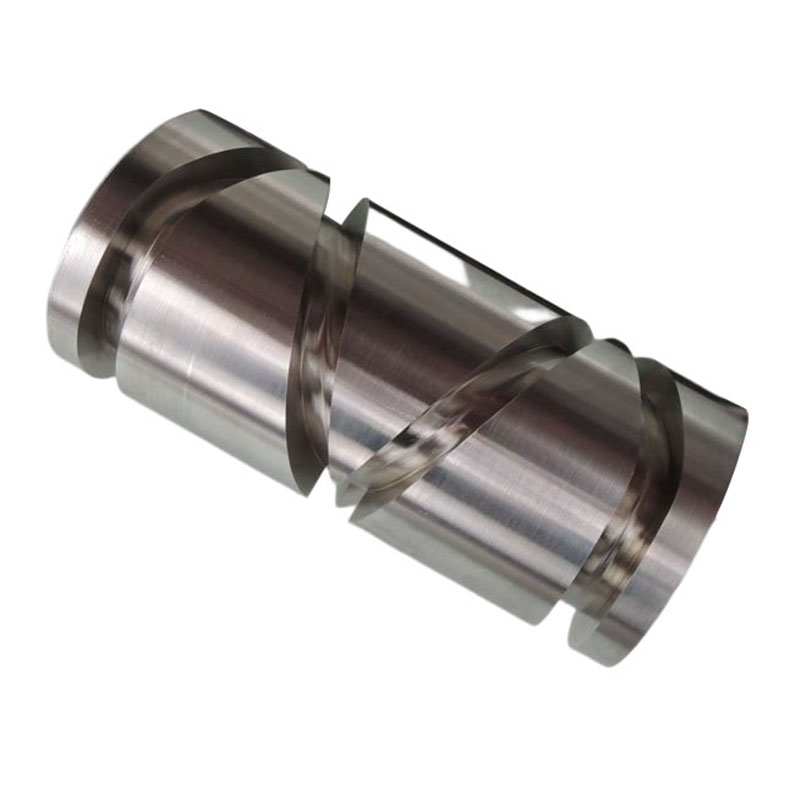
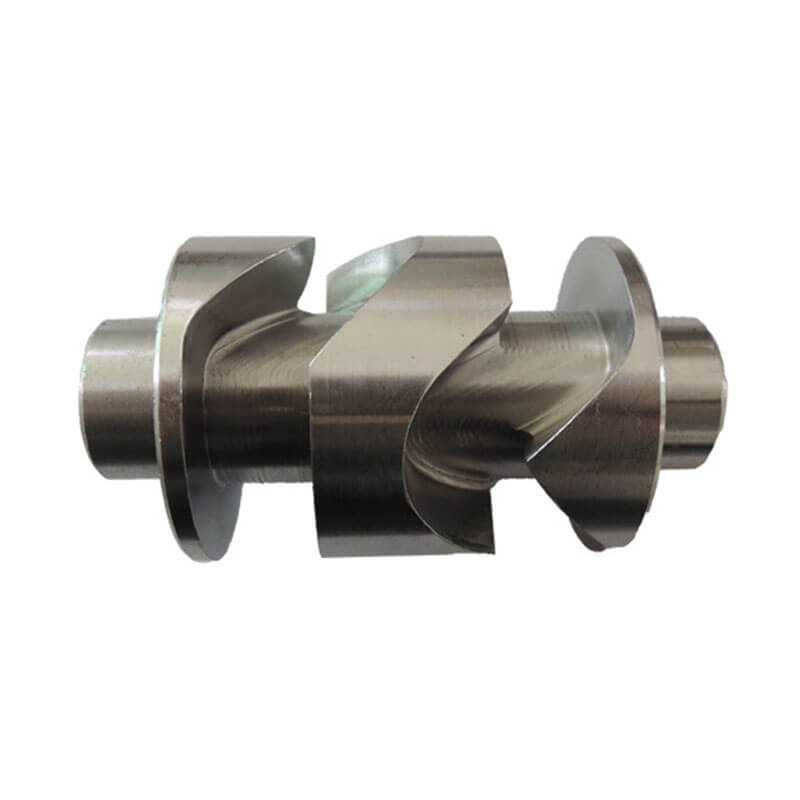
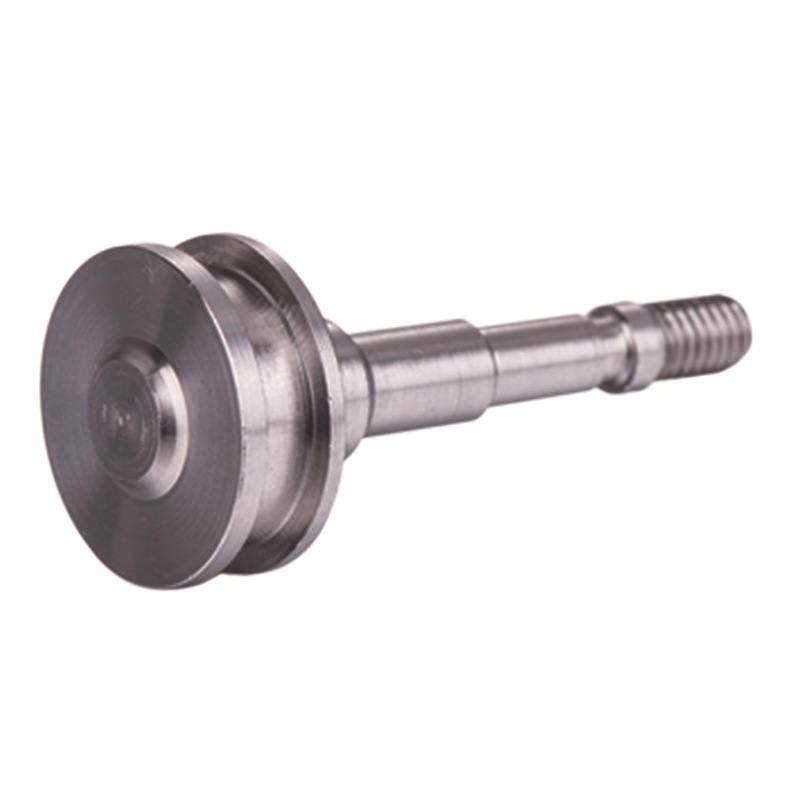
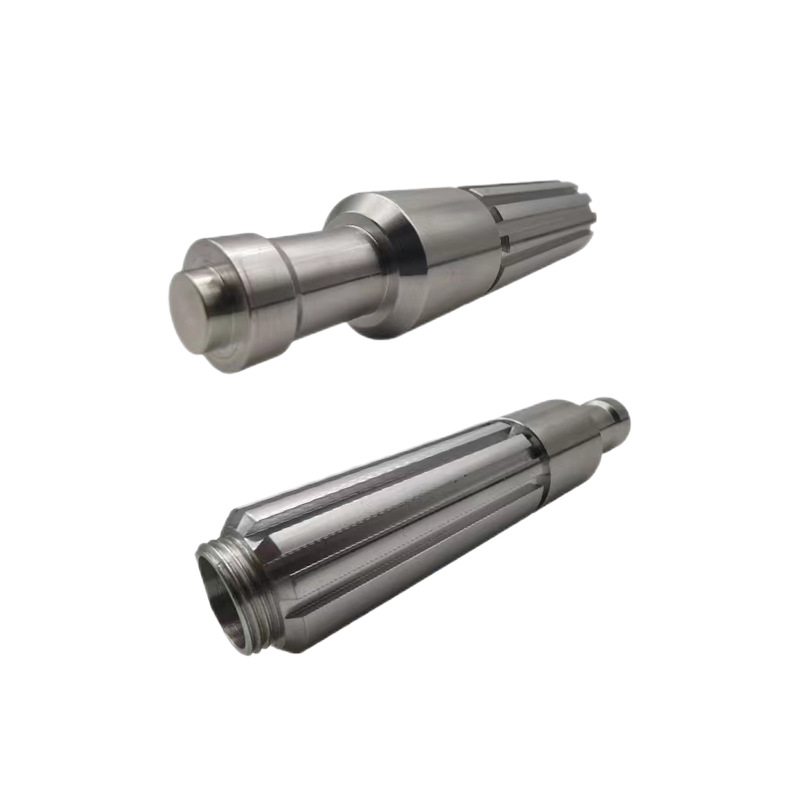
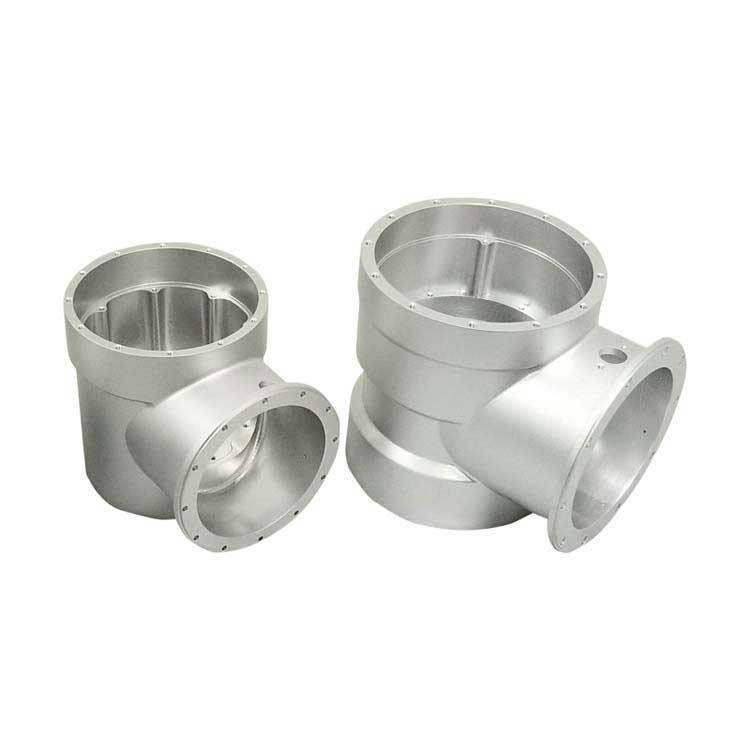
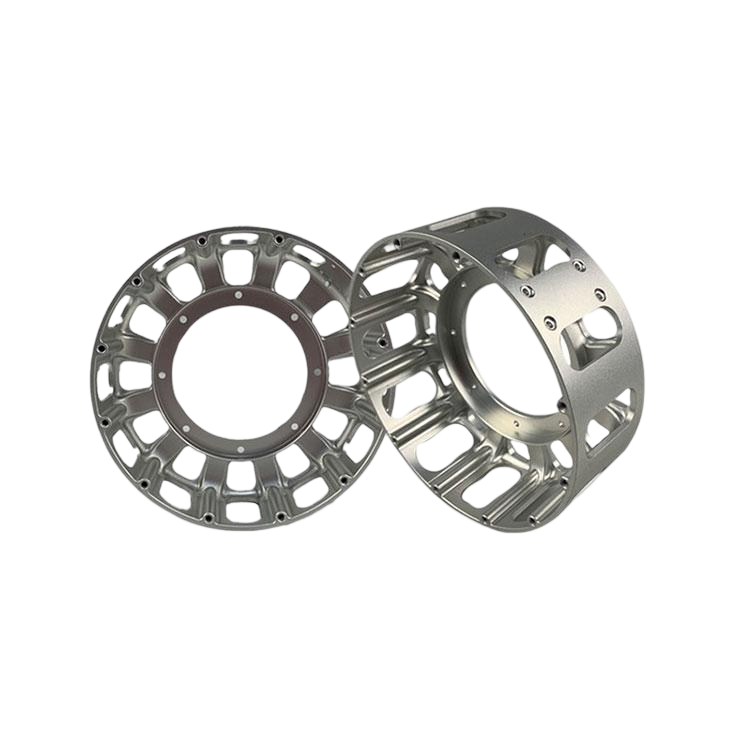
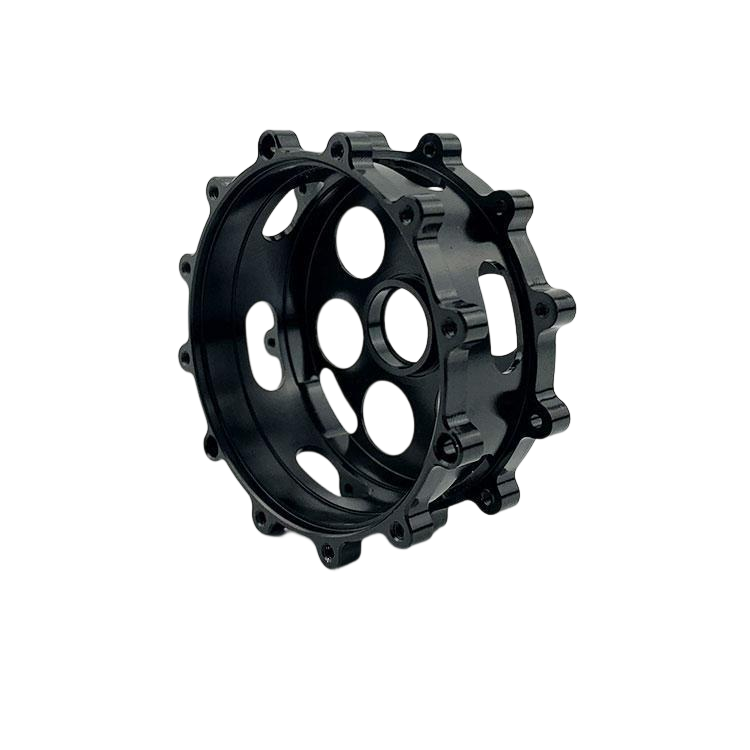
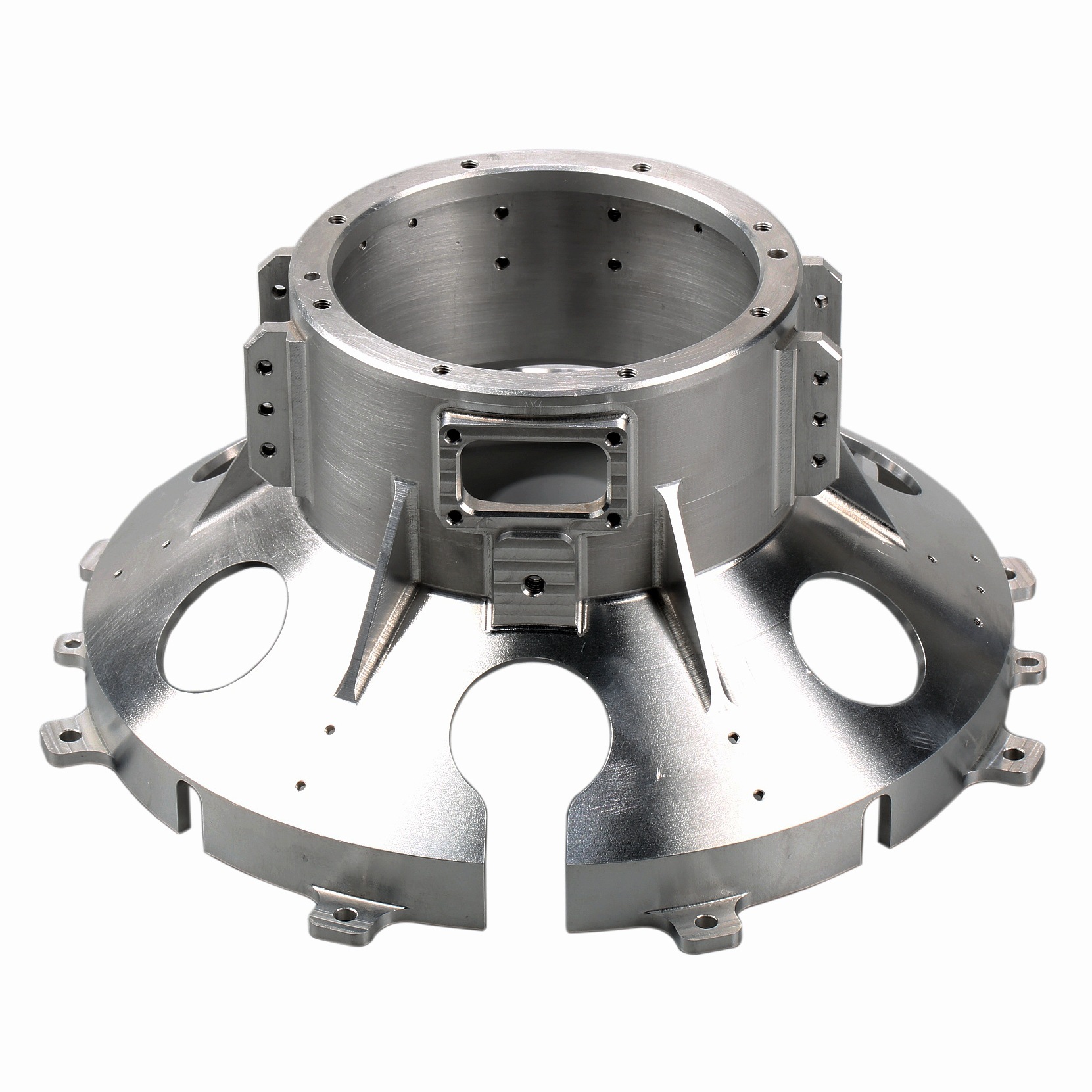
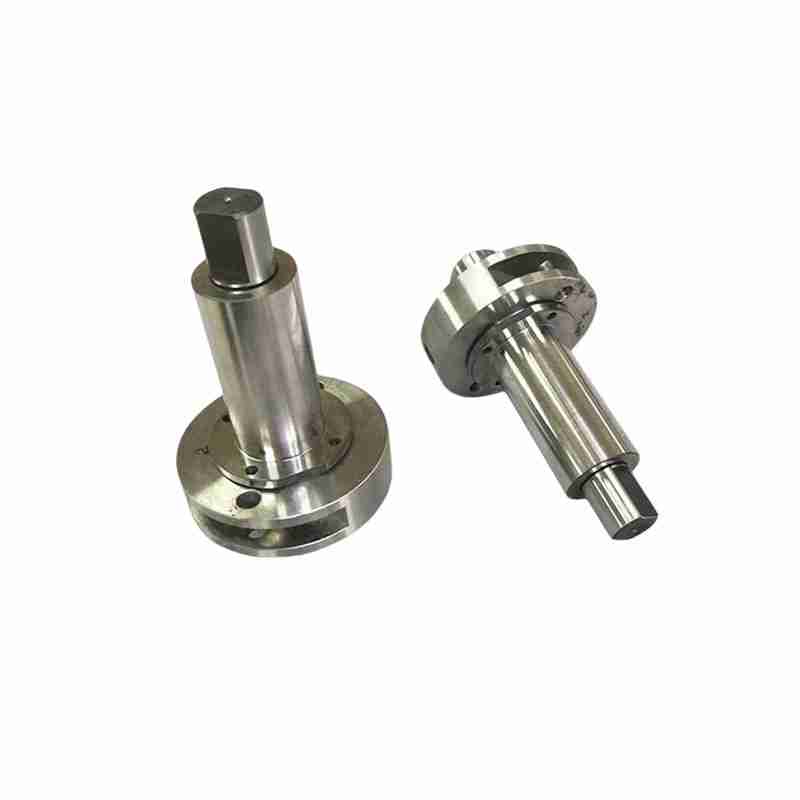
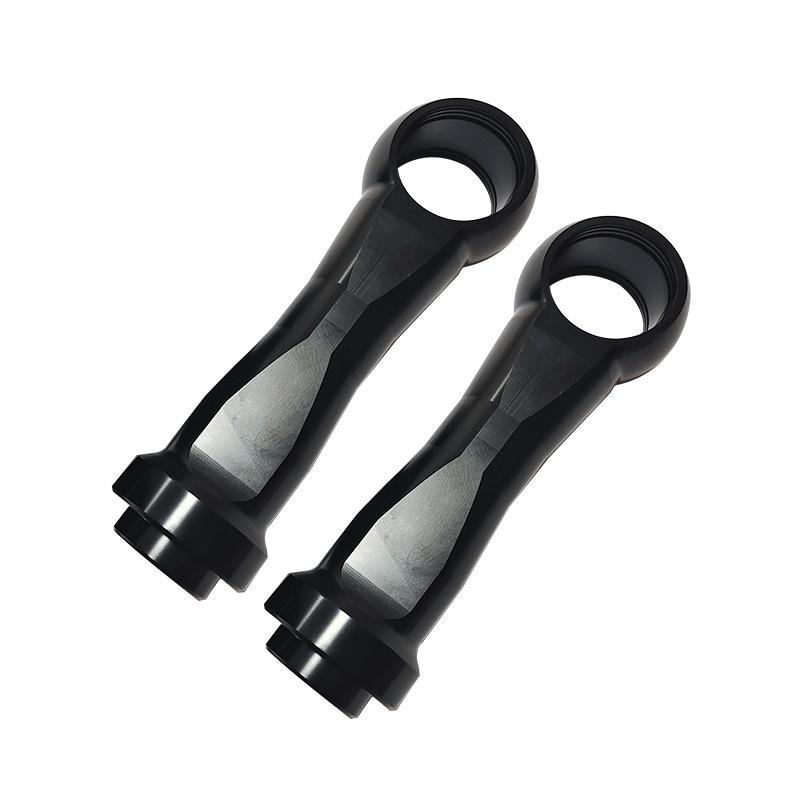
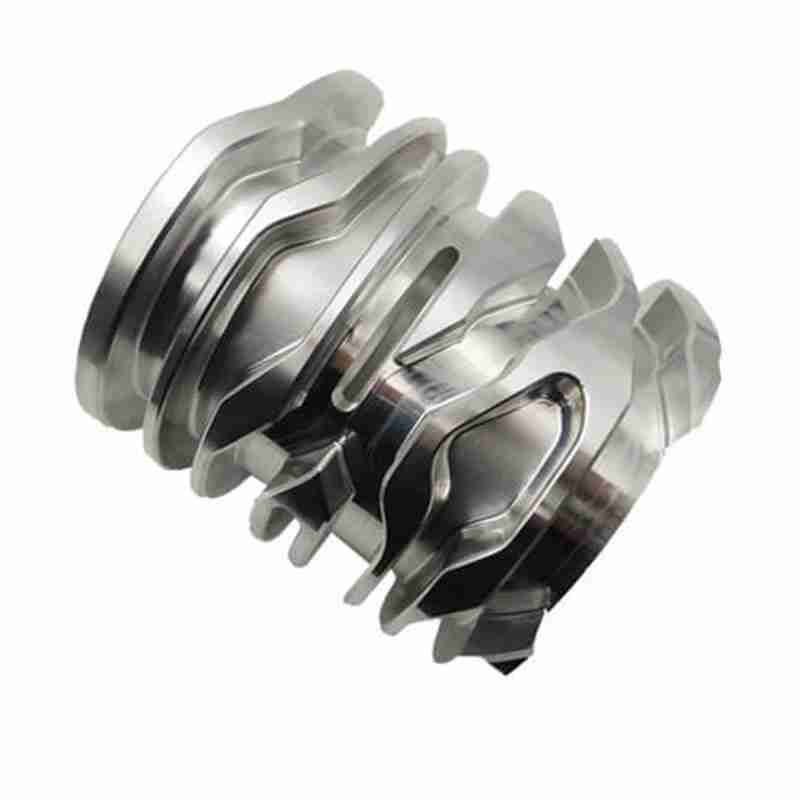






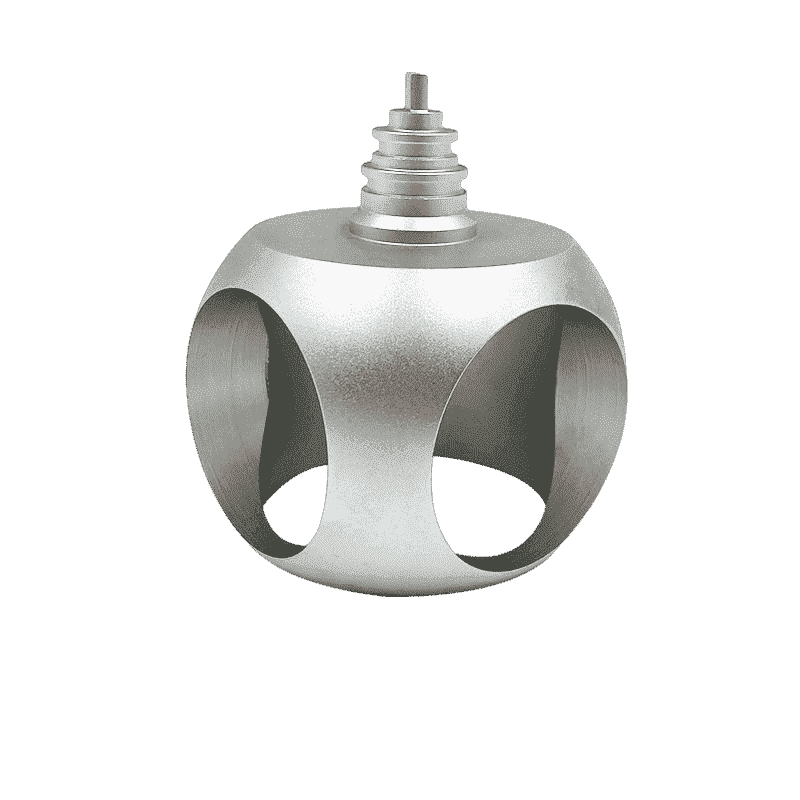




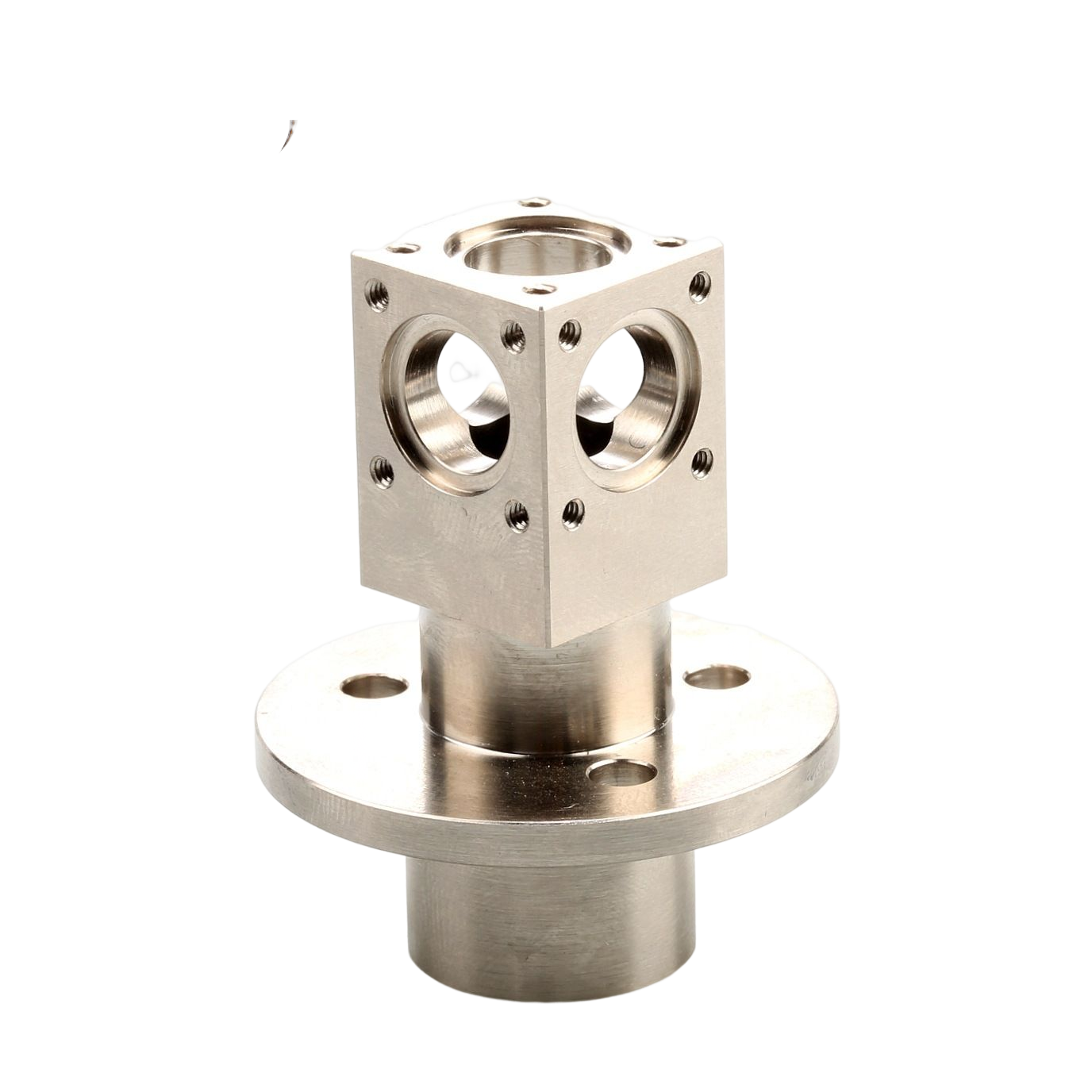




What Sets Us Apart

Strong Experience
With 16 years of CNC turning milling parts machining expertise, we focus on high-quality, customized solutions for different CNC turning milling parts demands.

Advanced Machine
20 sets precision turning and milling lathe with mature and stable manufacturing processes with technical machinist and engineer. We could manufacture different mill turn machining parts to meet your need.

Surprised Price
Stockpiling a large amount of conventional materials and having a mature production process can reduce the overall price by 5%.

24/7 Engineering Support
Masion is specializing in offering 24/7 engineering support, design services, cost reduction, quality assurance, and smooth product transitionsunparalleled excellence etc.
CNC Turning milling parts Manufacturing Process

Raw Material
At different stages of material preparation, various materials such as aluminum, brass, copper, bronze, stainless steel, titanium, PEEK, POM, etc., can be chosen to manufacture custom Swiss Lathe Parts. Additionally, we offer regular product material inventory to address any issues related to insufficient delivery times.
Mill Turn Machining Parts Machining
- Milling
- Turning
- Drilling
- Threading
- Cutting
- Countersinking
- Boring
- Knurling
- Grooving
- Taper
- Tapping
- Reaming

Packing
- For mill turn machining parts. with extremely high requirements, we pack the part one by one with PC bag, or blister bag etc.
- For mill turn machining parts. with moderate requirements, we also perform packing the bag as clients need.

- For mill turn machining parts. with no packaging requirements, we will arrange the products neatly and separate them with cardboard.

Quality Control(Testing)
- Masion conduct material inspections to ensure the parts correctness.
- Masion perform initial inspections on the first samples; production proceeds only if the dimensional inspection is passed, with adjustments made if necessary for non-compliance.
- Masion conduct sample inspections on the manufactured products to ensure compliance with the dimensional requirements specified in the drawings.
Application Area






Mill Turn Machining Parts FAQs
Mill-turn machining is a process that combines both milling and turning operations in a single machine setup. This approach is commonly used in the manufacturing industry to create complex parts with multiple features. Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to mill-turn machining parts:
Mill-turn machining is a manufacturing process that integrates both milling and turning operations in a single machine setup.This approach allows for the production of complex parts with features that require both milling and turning processes. In traditional machining, milling and turning are separate processes performed on different machines. However, in mill-turn machining, a single machine, often referred to as a mill-turn center or a multitasking machine, is capable of performing both types of operations.
Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects of mill-turn machining:
Milling Operations:
Milling involves removing material from a workpiece using rotary cutters. This can include operations like contouring, slotting, drilling, and other processes that create complex shapes and features.
Turning Operations:
Turning is the process of rotating a workpiece on a spindle while a cutting tool removes material to create cylindrical shapes, such as shafts, discs, and other rotationally symmetric components.
Integrated Operations:
Mill-turn machines have the capability to seamlessly switch between milling and turning operations without requiring the removal of the workpiece. This integration is achieved through the use of multiple tool turrets, spindles, and sophisticated control systems.
Reduced Setup Time:
One of the primary advantages of mill-turn machining is the reduction in setup time. Since both milling and turning operations can be performed in a single setup, there is no need to transfer the workpiece between different machines, leading to increased efficiency.
Complex Part Production:
Mill-turn machining is particularly well-suited for the production of complex parts that require a combination of milling and turning features. This includes components with intricate geometries, multiple surfaces, and features that would be challenging or impractical to produce with separate milling and turning processes.
Multi-Axis Capability:
Many mill-turn machines are equipped with multiple axes, allowing for simultaneous machining on different planes. This capability is especially useful for creating contoured surfaces and complex 3D shapes.
Tool Changes:
Mill-turn machines often incorporate automatic tool changers that allow for quick and efficient switching between different milling and turning tools. This contributes to the overall versatility of the machining process.
Precision and Accuracy:
The integration of milling and turning operations in a single setup enhances precision and accuracy, as the relative positions of features on the workpiece can be maintained without the need for repositioning.
Mill-turn machining is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and others where the production of complex and high-precision components is essential. The technology continues to evolve, with modern mill-turn machines offering advanced features and capabilities to meet the demands of increasingly complex manufacturing requirements.
Mill-turn machining offers several advantages, making it a preferred choice in various manufacturing applications. Here are some key advantages:
Reduced Setup Time:
Mill-turn machining allows for the completion of both milling and turning operations in a single setup. This eliminates the need to transfer the workpiece between different machines, reducing overall setup time and increasing efficiency.
Improved Accuracy and Precision:
Performing milling and turning operations in the same setup enhances accuracy and precision. The relative positions of features on the workpiece are maintained without the errors introduced by multiple setups.
Enhanced Flexibility:
Mill-turn machines are highly versatile and can handle a wide range of machining operations. This flexibility is beneficial for manufacturers dealing with diverse parts and components.
Complex Part Production:
Mill-turn machining is ideal for producing complex parts with intricate geometries and a combination of milling and turning features. It is particularly well-suited for components with multiple surfaces and contours.
Improved Surface Finish:
The integrated nature of mill-turn machining allows for smoother transitions between milling and turning operations, contributing to improved surface finish on the final part.
Space and Cost Savings:
Combining milling and turning capabilities into a single machine reduces the need for separate machines for each operation. This can result in significant space savings in the manufacturing facility and potentially lower equipment costs.
Simultaneous Multi-Axis Machining:
Many mill-turn machines are equipped with multiple axes, enabling simultaneous machining on different planes. This capability is especially useful for creating complex 3D shapes and contoured surfaces.
Reduced Work-in-Progress Inventory:
Since mill-turn machining allows for the completion of a part in a single setup, there is less work-in-progress inventory. This can lead to improved production flow and better management of manufacturing resources.
Streamlined Programming:
Modern mill-turn machines often come with advanced control systems that streamline programming. This includes features like CAD/CAM integration, toolpath optimization, and simulation, making it easier for operators to program and monitor the machining process.
Increased Throughput and Productivity:
The efficiency gained from reduced setup times, simultaneous machining, and the ability to handle multiple operations in one setup contribute to increased throughput and overall productivity.
Quick Tool Changes:
Mill-turn machines often feature automatic tool changers, allowing for rapid switching between different tools. This minimizes downtime associated with manual tool changes.
In summary, mill-turn machining offers a comprehensive solution for manufacturers seeking increased efficiency, precision, and flexibility in the production of complex parts. The advantages of reduced setup time, improved accuracy, and the ability to handle diverse machining operations make it a valuable technology in modern manufacturing environments.
Mill-turn machining is particularly well-suited for the production of complex parts that require a combination of milling and turning operations. The versatility of mill-turn machines makes them suitable for a wide range of parts across various industries. Here are some types of parts that are commonly produced using mill-turn machining:
Aerospace Components:
Mill-turn machining is widely used in the aerospace industry for manufacturing components such as turbine shafts, engine mounts, landing gear parts, and other complex aerospace components that require precise milling and turning operations.
Medical Implants:
The medical industry often relies on mill-turn machining for the production of medical implants, such as orthopedic implants and joint replacements. These components may have intricate shapes and require high precision.
Automotive Parts:
Automotive manufacturers use mill-turn machining for the production of various components, including shafts, gears, axles, and other parts with complex geometries. The efficiency of mill-turn machining is beneficial for mass production.
Tooling and Dies:
Mill-turn machining is employed in the production of tooling and dies used in manufacturing processes. This includes molds, cutting tools, and dies with complex contours and features.
Oil and Gas Components:
Parts used in the oil and gas industry, such as valves, connectors, and drilling components, often require precision machining. Mill-turn machining is capable of producing these components efficiently.
Electronic Components:
Mill-turn machining is used to produce intricate electronic components, such as connectors, housings, and other parts with precise features. The ability to combine milling and turning operations in a single setup is advantageous for producing complex electronic components.
Complex Shafts and Rotors:
Mill-turn machining is well-suited for the production of complex shafts and rotors used in various applications, including industrial machinery, power generation, and transportation.
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Components:
Components for hydraulic and pneumatic systems, such as cylinders, pistons, and valves, often require both milling and turning operations. Mill-turn machining is effective in producing these components with high precision.
Precision Machined Parts:
Mill-turn machining is suitable for a wide range of precision machined parts, including those with tight tolerances, intricate features, and a need for a smooth surface finish.
Customized and Low-Volume Parts:
Mill-turn machining is adaptable to the production of customized and low-volume parts. The ability to perform multiple operations in one setup makes it efficient for producing prototypes and small batches of specialized components.
Overall, mill-turn machining is a versatile solution for the production of parts with complex geometries, multiple features, and a combination of milling and turning requirements. Its applications span across various industries, meeting the demands of modern manufacturing for efficiency and precision.
Mill-turn machining is a versatile process that can be applied to a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the part being produced and the capabilities of the mill-turn machine. Here are some common materials that can be processed using mill-turn machining:
Metals:
Steel: Carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel are commonly machined using mill-turn processes. These materials are prevalent in various industries, including automotive and aerospace.
Aluminum: Mill-turn machining is well-suited for aluminum components, offering efficiency and precision. Aluminum is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.
Brass: Brass components, such as fittings and connectors, can be machined using mill-turn processes. Brass is known for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
Titanium: Mill-turn machining is used for titanium components in aerospace, medical, and industrial applications. Titanium’s strength and lightness make it a popular choice in challenging environments.
Plastics:
Nylon: Mill-turn machining is suitable for producing parts from nylon, a thermoplastic known for its durability and low friction properties. Nylon is used in various industries, including automotive and consumer goods.
Acrylic (PMMA): Mill-turn processes can be applied to acrylic, a transparent thermoplastic often used for components in optical and display applications.
Polyethylene (PE) and Polypropylene (PP): These thermoplastics are commonly used in the production of components for the packaging, automotive, and consumer goods industries.
Composites:
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRP): Mill-turn machining is used for processing composite materials like CFRP, which are prevalent in aerospace and automotive applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastics (FRP): FRP components, often used in construction, marine, and automotive applications, can be machined using mill-turn processes.
Other Materials:
Copper: Mill-turn machining can be used for copper components, such as electrical connectors and conductors.
Bronze: Bronze, an alloy of copper, can be machined using mill-turn processes for applications in bearings, bushings, and decorative items.
Inconel and Other Super Alloys: Mill-turn machining is employed for materials like Inconel, Hastelloy, and other high-temperature and corrosion-resistant super alloys used in aerospace, chemical, and petrochemical industries.
It’s important to note that the specific capabilities of the mill-turn machine, including spindle speed, cutting tool materials, and coolant systems, will influence the choice of materials that can be effectively processed. Additionally, the choice of material depends on the requirements of the final part, such as mechanical properties, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
CNC turning milling parts cost is a critical concern for all customers, and finding a supplier with both qualified quality and competitive prices is essential. Several key factors influence the cost of CNC turning milling parts, and analyzing these factors can lead to a quick conclusion.
Complexity of Parts:
The complexity of part design and features has a significant impact on costs. Parts with intricate geometries, tight tolerances, and multiple operations generally have higher manufacturing costs. While CNC turning milling can efficiently handle complex products, its relative pricing is often lower compared to conventional turning and milling processes due to its ability to rapidly process various complex surfaces.
Material Costs:
The type and quality of materials used determine overall costs. Different materials have varying costs per unit volume, and special materials may be more expensive. When selecting materials, we aim for cost-effective options that meet the required performance criteria. Typically, aluminum alloy processing is more economical compared to stainless steel, copper, or titanium alloy processing.
Processing Time:
The time required for CNC turning and milling operations directly impacts costs. Complex or lengthy machining operations result in higher production costs. However, with our extensive experience in CNC turning milling, we can optimize the processing time for complex products to ensure cost-effectiveness. Generally, machining costs are calculated at around $10 USD per hour.
Production Volume:
The quantity of parts being produced affects the cost per unit. Larger production runs often allow for economies of scale and reduced per-part costs. Despite our experience in small-batch processing, we maintain competitive prices, and for frequently used materials, we keep stock to ensure reasonable costs for small batches.
In conclusion, our cost quoting takes into account material costs, processing time, and a reasonable profit margin. We strive to provide accurate and competitive quotes to ensure that our pricing is both reasonable and competitive in the market. If you have specific projects or requirements, we can provide a customized quote based on your needs and specifications.
Free Sample
Explore Other Products

Swiss CNC Machining
Custom Swiss CNC turningTC4 titanium alloy Anodizingmedical dental nail bone nail.

CNC Milling
CNC Milling Aluminum different automobile hub, and different 3-axis, 4-axis,5 axis CNC machining parts.

CNC Turning
Stainless Steel stethoscope Chestpiece and another different CNC turning Parts.


